Organizations can’t ignore the need for training. New skills and methods are required as advanced technologies and employee diversity transforms the workplace. More and more, people are drawn to expand their proficiencies, whether for job requirements or personal needs.
What are the methodologies educators must learn to apply in the adult classroom? One effective approach is androgogy (student-centred learning), which has its own set of guiding principles that differ from traditional pedagogy (teacher-centred learning). One can teach androgogically with children, though this is not done in the traditional classroom. One can also teach pedagogically with adults – which is the usual format in a university.
Adult-centred teaching takes into account the different backgrounds and learning stages of its pupils. It is highly flexible and centred on the needs of the learners, rather than simply obeying a curriculum. Instructors must respect that the adult student has accumulated knowledge and experience.
Relevant, applicable education that can be put to use to solve real-life problems is needed. In this way, the teacher is more of a guide than a leader. Students will exercise their own choices in the class curriculum and structure. The adult-learning experience is enhanced as students interact with each other, learning from their fellow students as they engage in class discussions and assess each other and themselves.
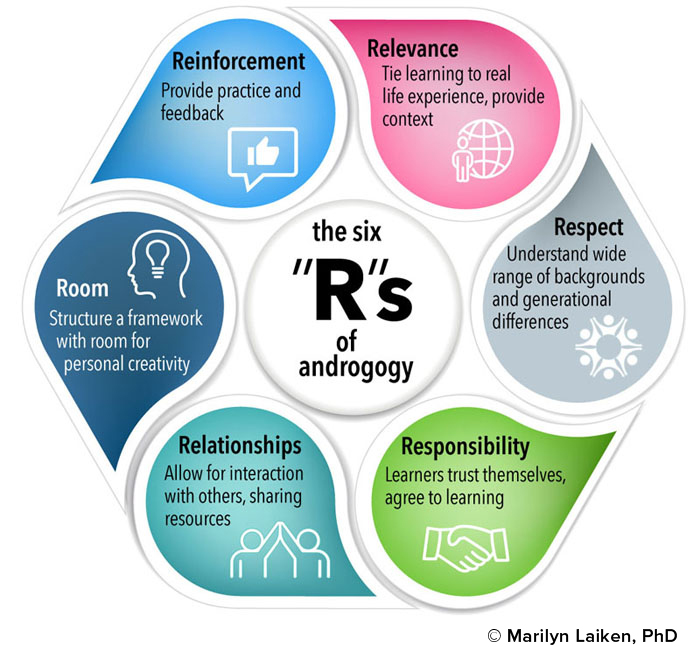
The following chart illustrates six of the most important concepts of androgogy.
—–
This material has been drawn in part from Schulich ExecEd’s upcoming program Masters Certificate in Adult Training and Development (starting Jan. 23, 2019). The program is designed to provide both leading-edge research and practical experience in teaching and training adults in the workplace. Participants learn to approach teaching/learning androgogically – or in a student-centred way, using experiential methodologies.